Bioengineering, Free Full-Text
By A Mystery Man Writer
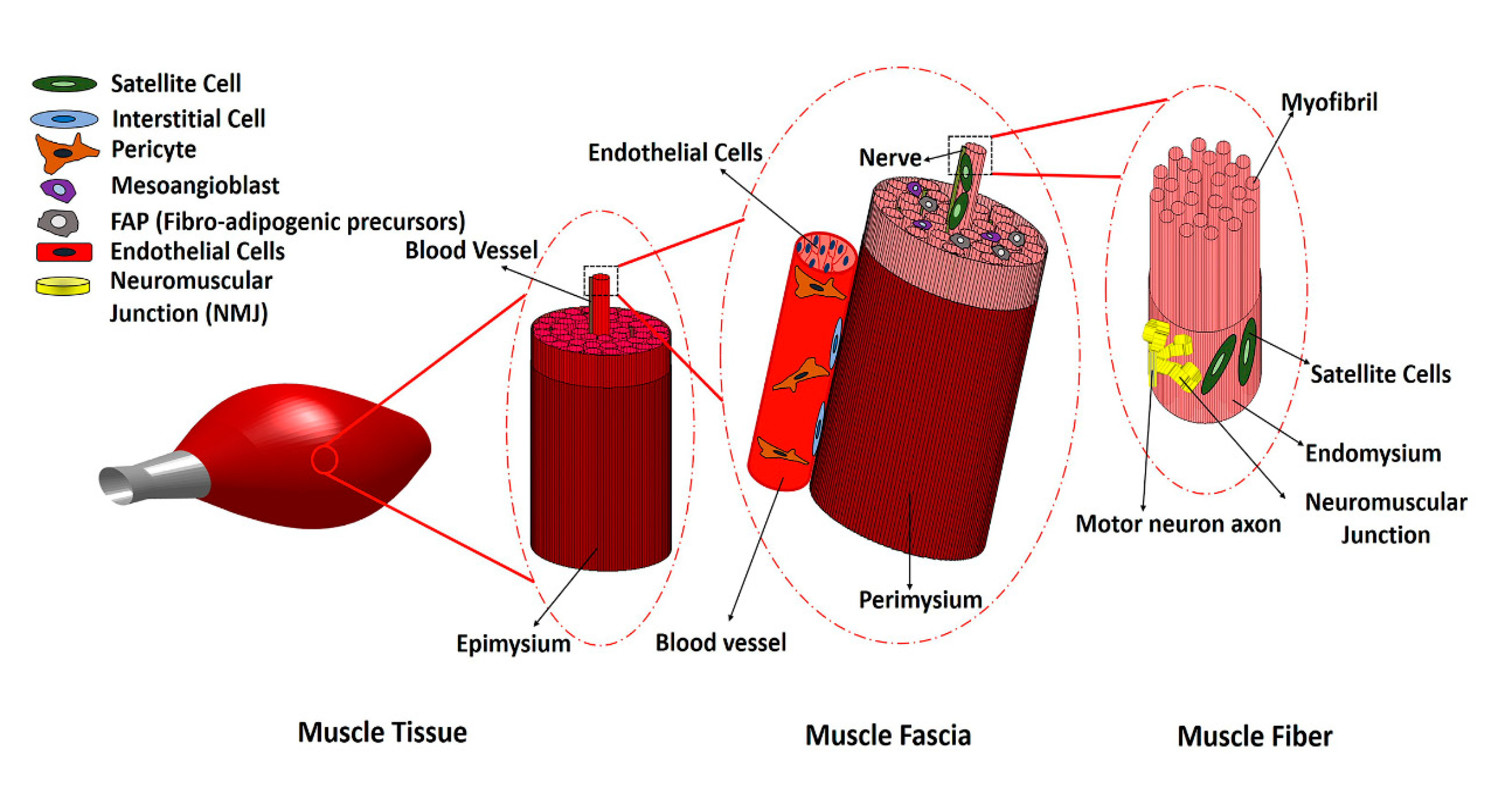
Extensive damage to skeletal muscle tissue due to volumetric muscle loss (VML) is beyond the inherent regenerative capacity of the body, and results in permanent functional debilitation. Current clinical treatments fail to fully restore native muscle function. Recently, cell-based therapies have emerged as a promising approach to promote skeletal muscle regeneration following injury and/or disease. Stem cell populations, such as muscle stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), have shown a promising capacity for muscle differentiation. Support cells, such as endothelial cells, nerve cells or immune cells, play a pivotal role in providing paracrine signaling cues for myogenesis, along with modulating the processes of inflammation, angiogenesis and innervation. The efficacy of cell therapies relies on the provision of instructive microenvironmental cues and appropriate intercellular interactions. This review describes the recent developments of cell-based therapies for the treatment of VML, with a focus on preclinical testing and future trends in the field.

McMaster School of Biomedical Engineering – Faculty of Engineering
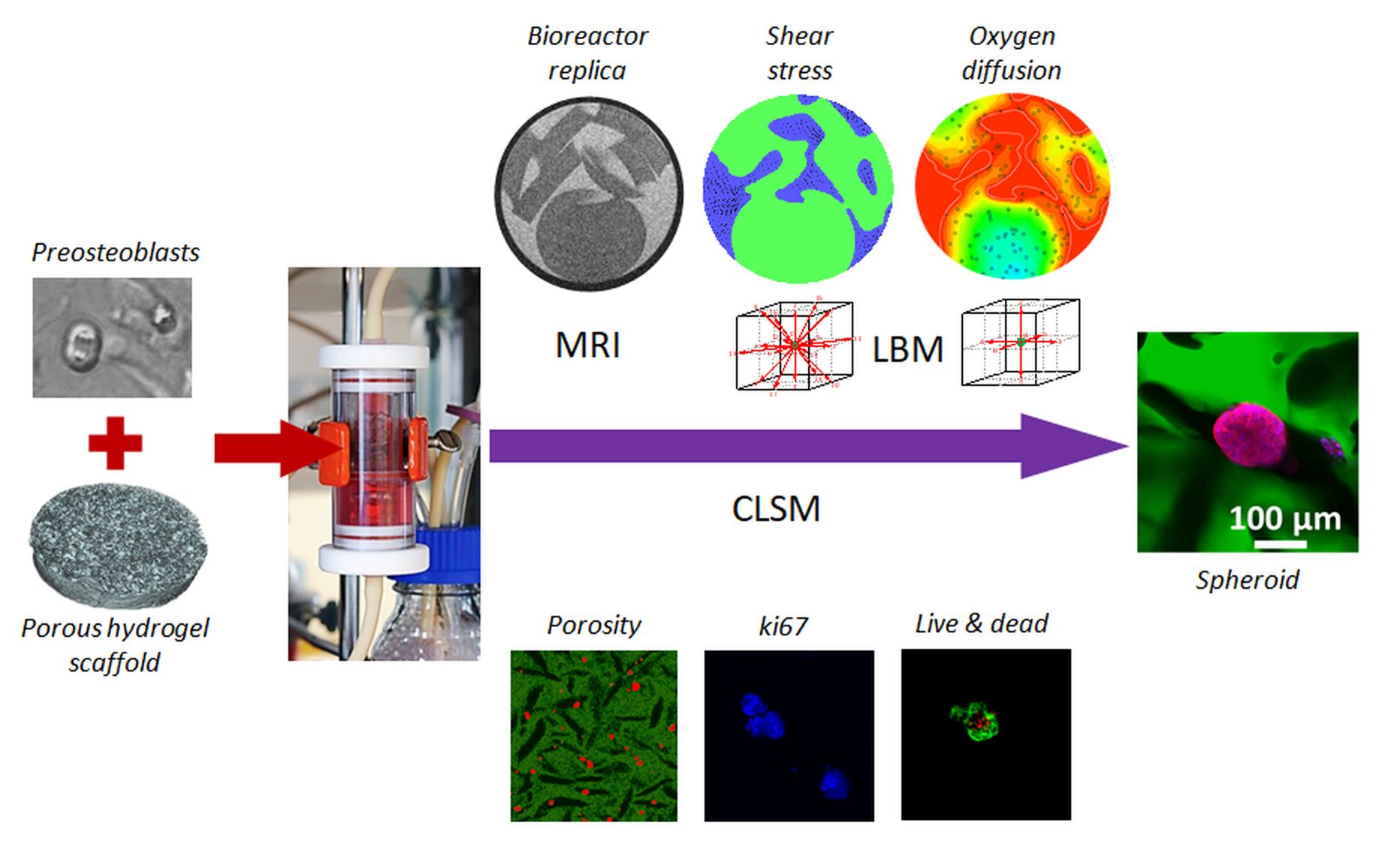
Bioengineering, Free Full-Text

BSc in Biomedical Engineering and Biotechnology - Khalifa University

Top 10 biomedical engineering jobs and who's hiring

I present to you the HORUS DRYAD licence, a primal biotech support
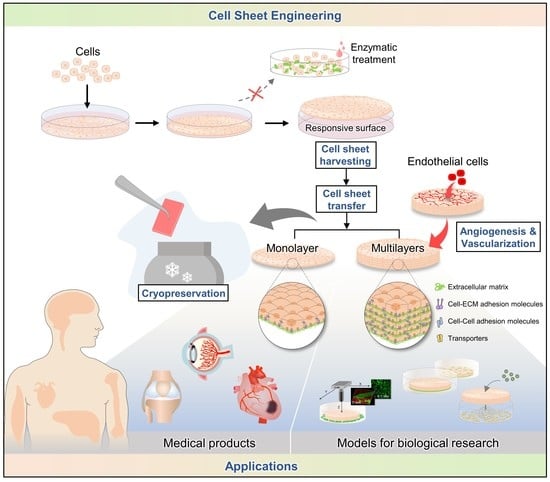
The Preclinical And Clinical Progress Of Cell Sheet, 41% OFF
Bioengineering, Free Full-Text
pub.mdpi-res.com/bioengineering/bioengineering-10
Mit School Of Bioengineering Sciences And Research Free Seminar Ad

Reasonably Priced Richness Abrazo Health using AI-powered EEG system for seizure detection, seizure monitor for adults
Bioengineering, Free Full-Text

Bioengineering, Free Full-Text
- Fingerhut - Maidenform Women's Sexy Must-Haves Lace Thong
- Tammy Slaton Jokes That She's a 'Diet Soda Ambassador' After Dramatic Weight Loss
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(674x259:676x261)/tammy-slaton-diet-coke-051923-4a213dddab7043cf9517d554a91c34e4.jpg)
- Summer Korean Style Solid Color Elegant Fashion Wide Leg Pants

- CHILL ATMOSPHERE FLARE HI-RISE LEGGING
- UOFON Thermal Tights Women Pantyhose Leggings Fleece Warm Fleece Lined Black Tights at Women's Clothing store