Cells, Free Full-Text
By A Mystery Man Writer
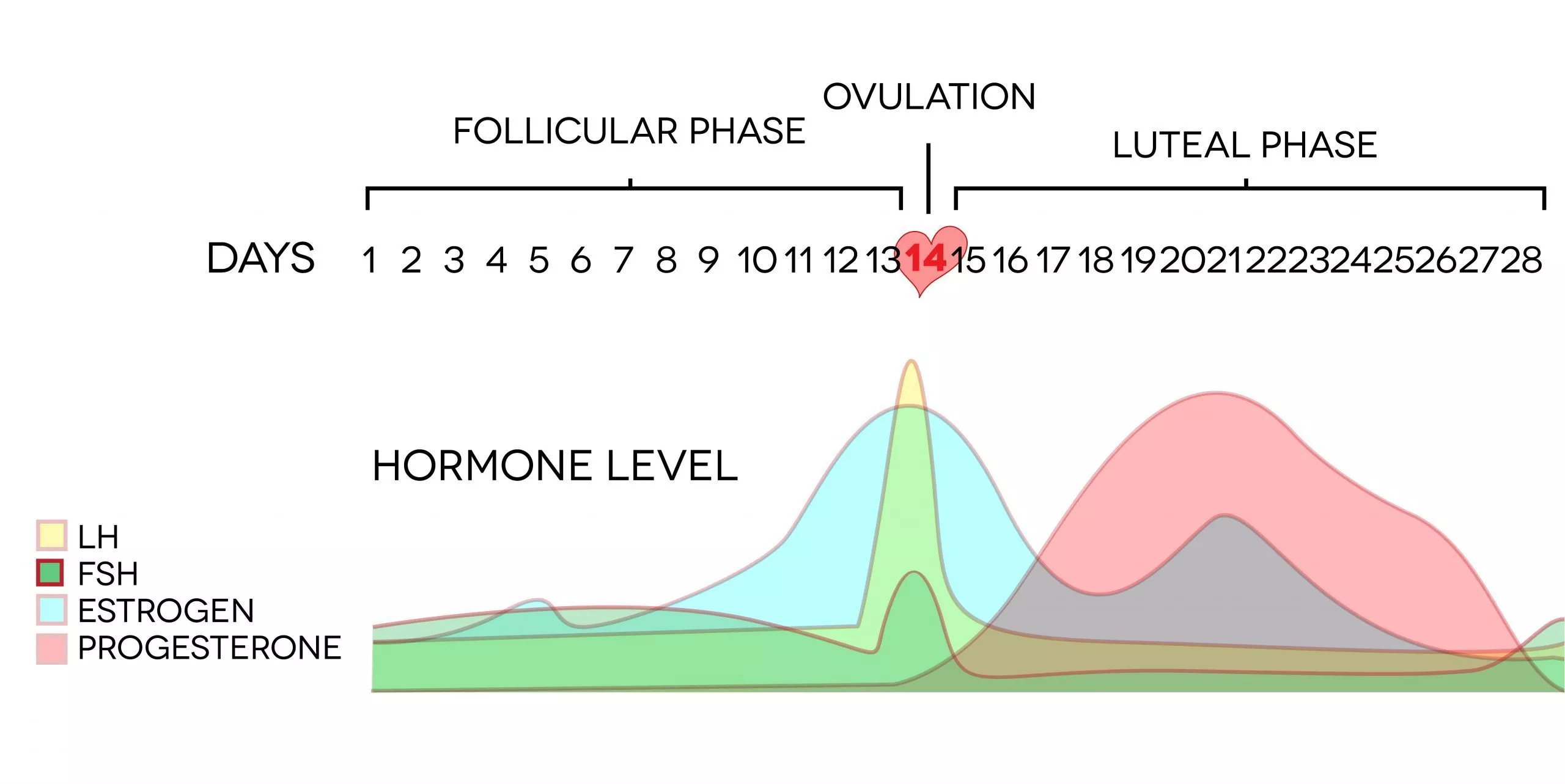
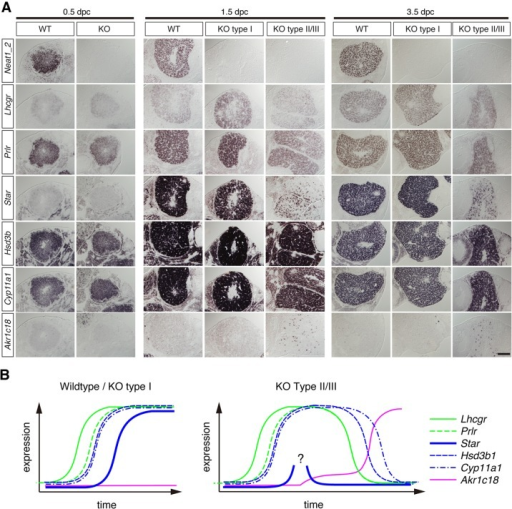
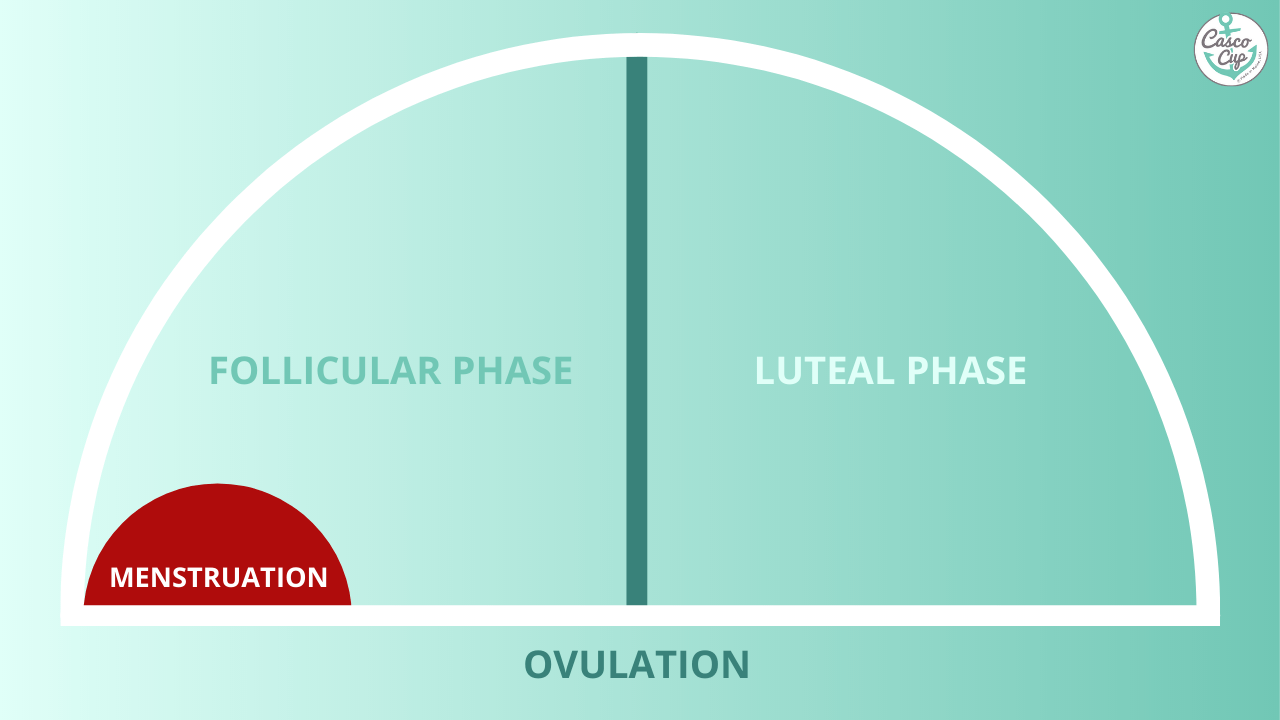
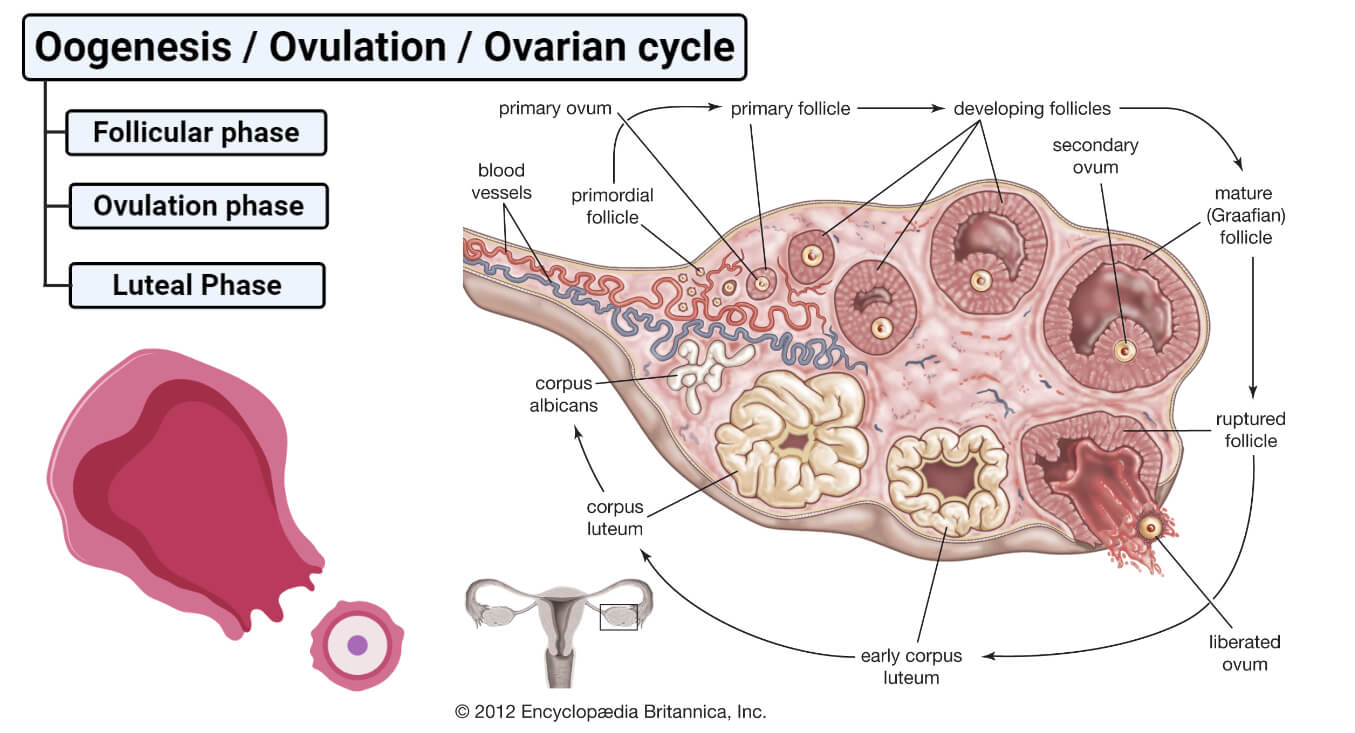
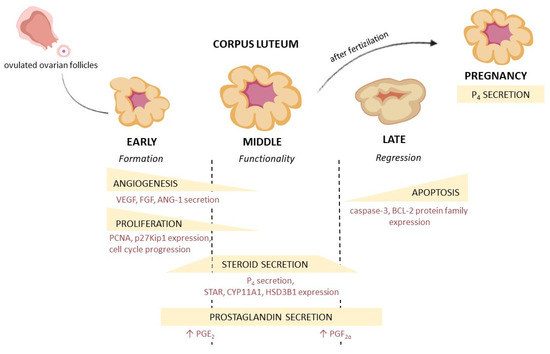
The corpus luteum is a small gland of great importance because its proper functioning determines not only the appropriate course of the estrous/menstrual cycle and embryo implantation, but also the subsequent maintenance of pregnancy. Among the well-known regulators of luteal tissue functions, increasing attention is focused on the role of neuropeptides and adipose tissue hormones—adipokines. Growing evidence points to the expression of these factors in the corpus luteum of women and different animal species, and their involvement in corpus luteum formation, endocrine function, angiogenesis, cells proliferation, apoptosis, and finally, regression. In the present review, we summarize the current knowledge about the expression and role of adipokines, such as adiponectin, leptin, apelin, vaspin, visfatin, chemerin, and neuropeptides like ghrelin, orexins, kisspeptin, and phoenixin in the physiological regulation of the corpus luteum function, as well as their potential involvement in pathologies affecting the luteal cells that disrupt the estrous cycle.
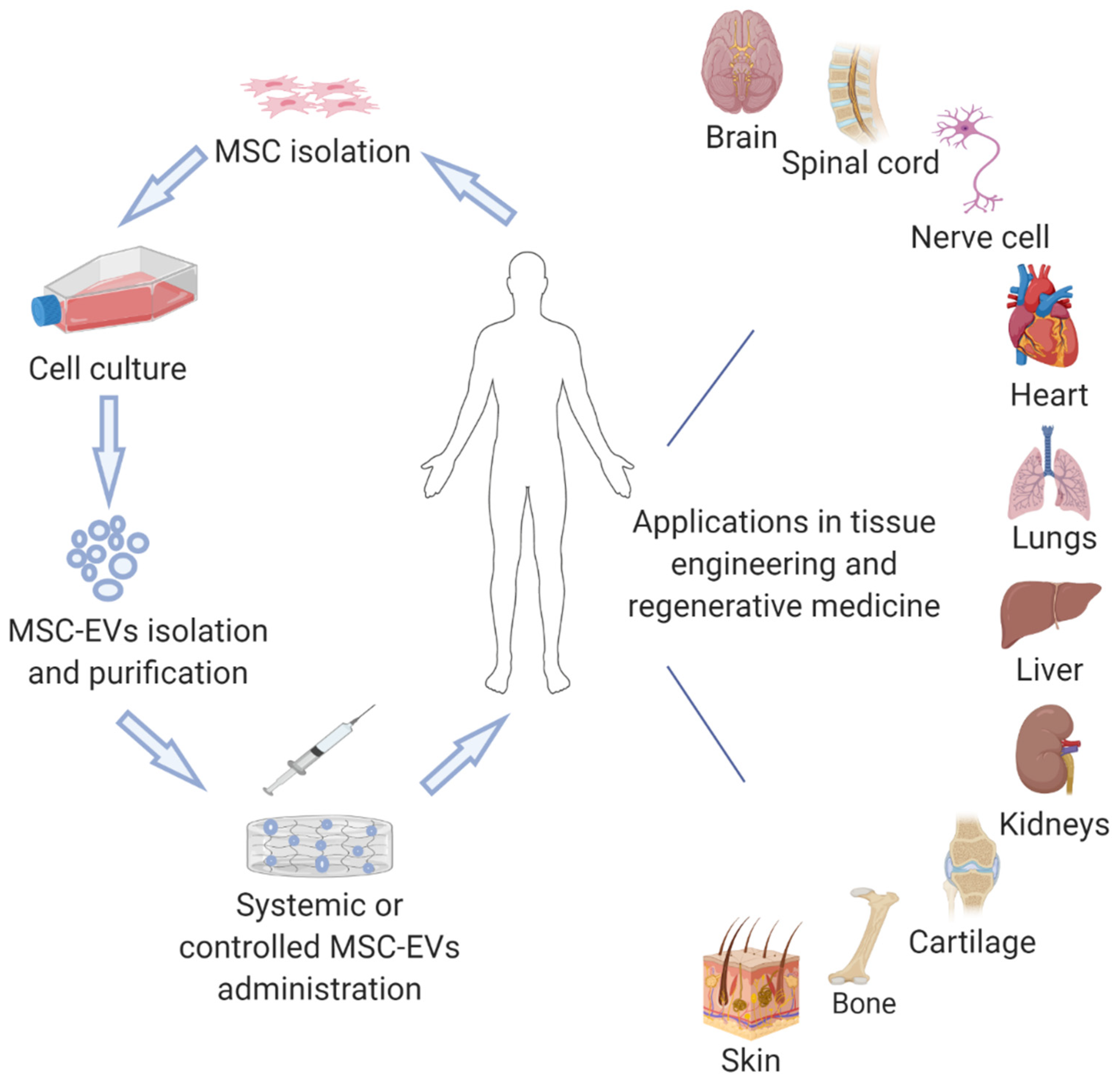
Characterizing human mesenchymal stromal cells' immune-modulatory

How to Make All Cells the Same Size in Excel? (5 Common Methods
Cells, Free Full-Text
Cells Free Full Text Hepatitis B Virus Entry Into Cells 19030
Cells, Free Full-Text, wr games cell
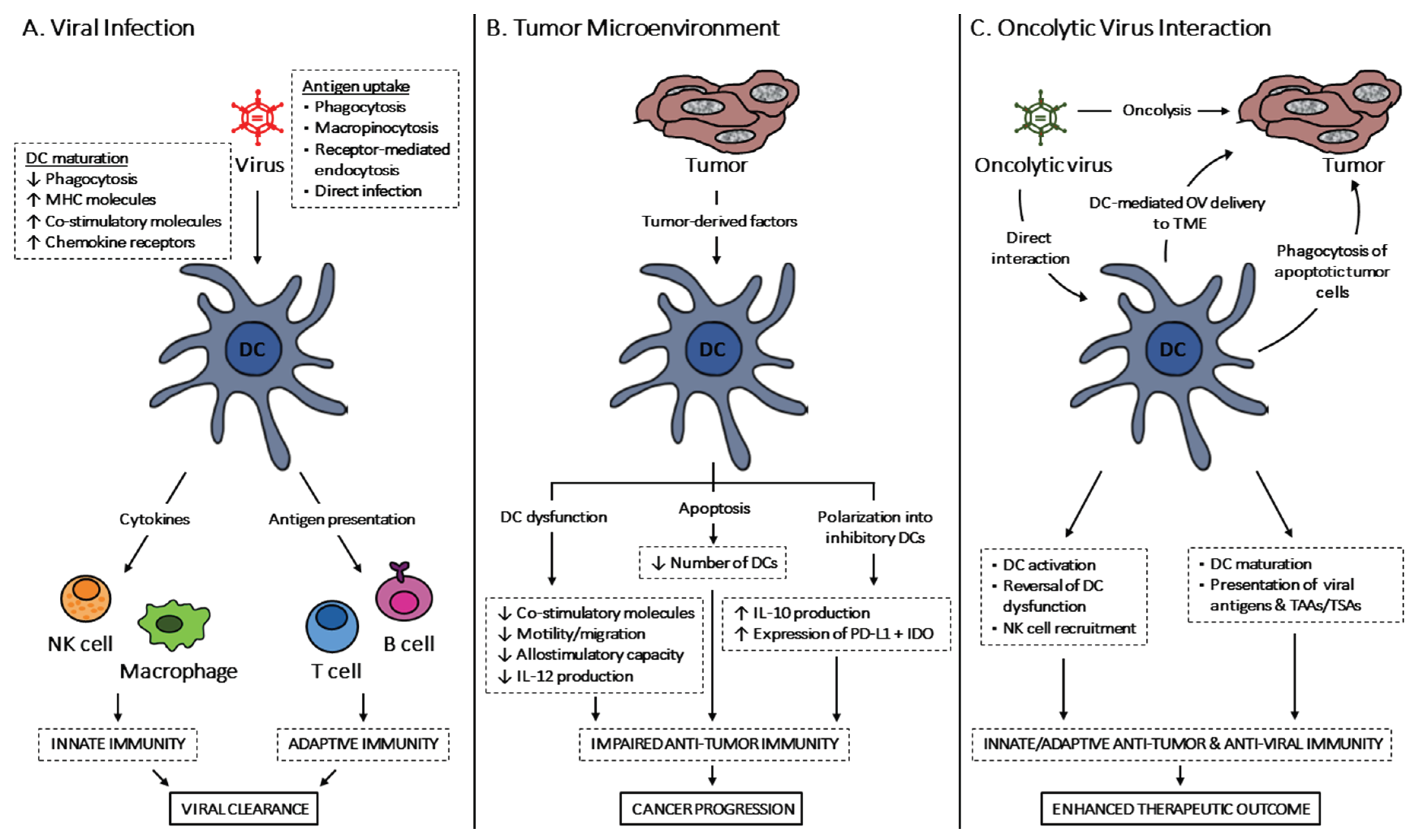
Viruses, Free Full-Text

Early clinical experience using donor-derived cell-free DNA to

New Dead Cells Update Brings a Flood of Free Content from Classic
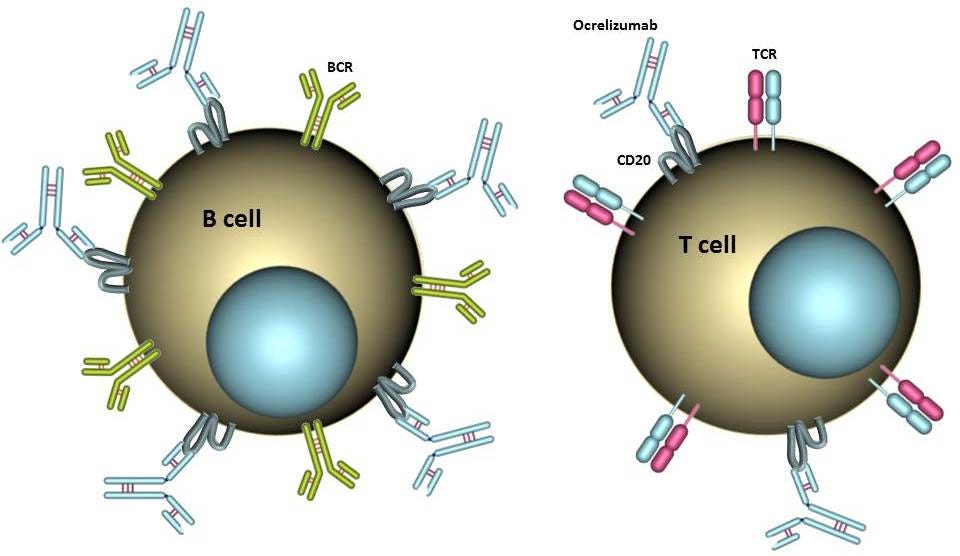
The case for antivirals targeting lytic EBV infection in MS
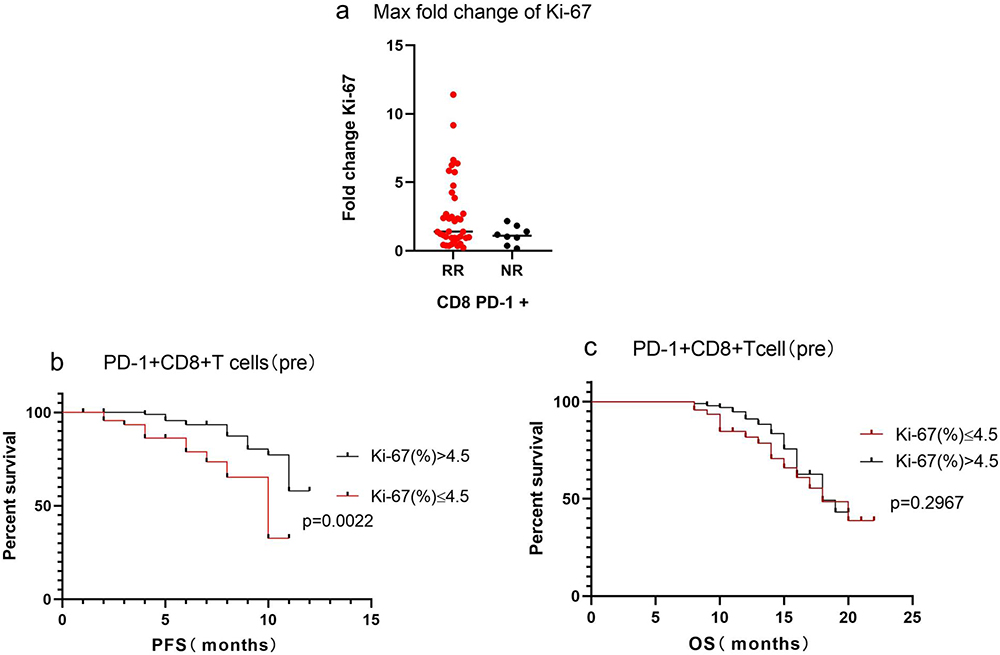
Cells, Free Full-Text, resultado lavoisier pcr
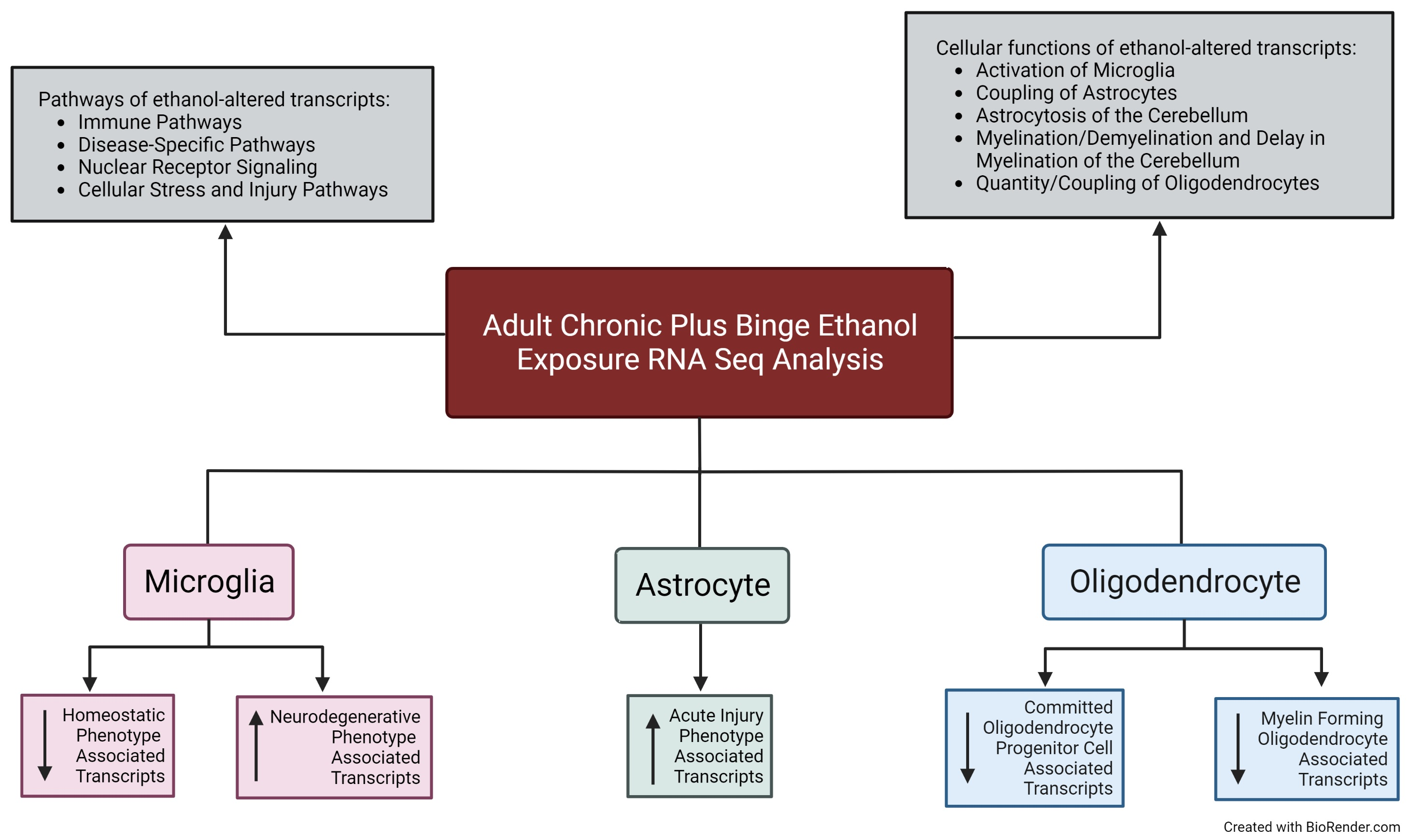
Cells, Free Full-Text
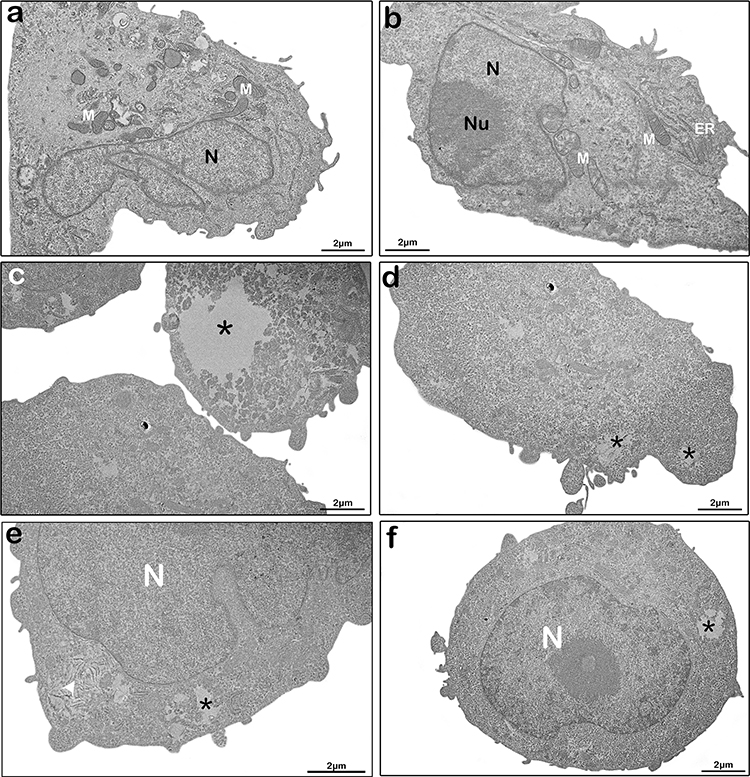
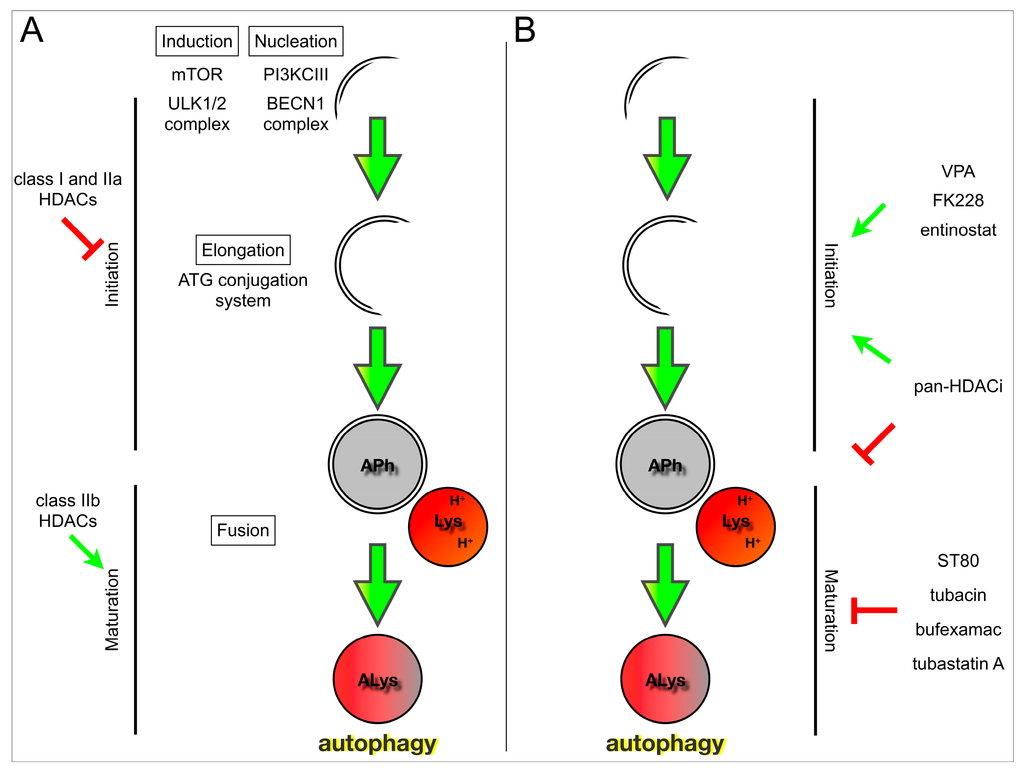
Tarin-loaded nanoliposomes activate apoptosis & autophagy
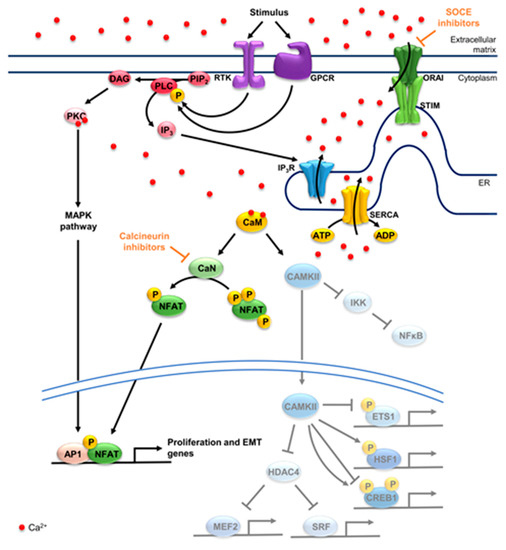
Images
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology on X: From May cover
- VTG Bankers Lamp Green Glass Shade Brass Base Pull-Chain Switch Desk/Library EXC

- Nike NBA Pro Combat Hyperstrong Compression Tights Pants 940259-100 Mens XXLTall

- Kendall Jenner's Errand-Running Outfit Will Make You Dig These
- FLY / VOADOR LIFE FITNESS (SOB CONSULTA) - Trade Fit

- Buy Women's Running Shoes Run Active - Grey Online