Medicina, Free Full-Text
By A Mystery Man Writer
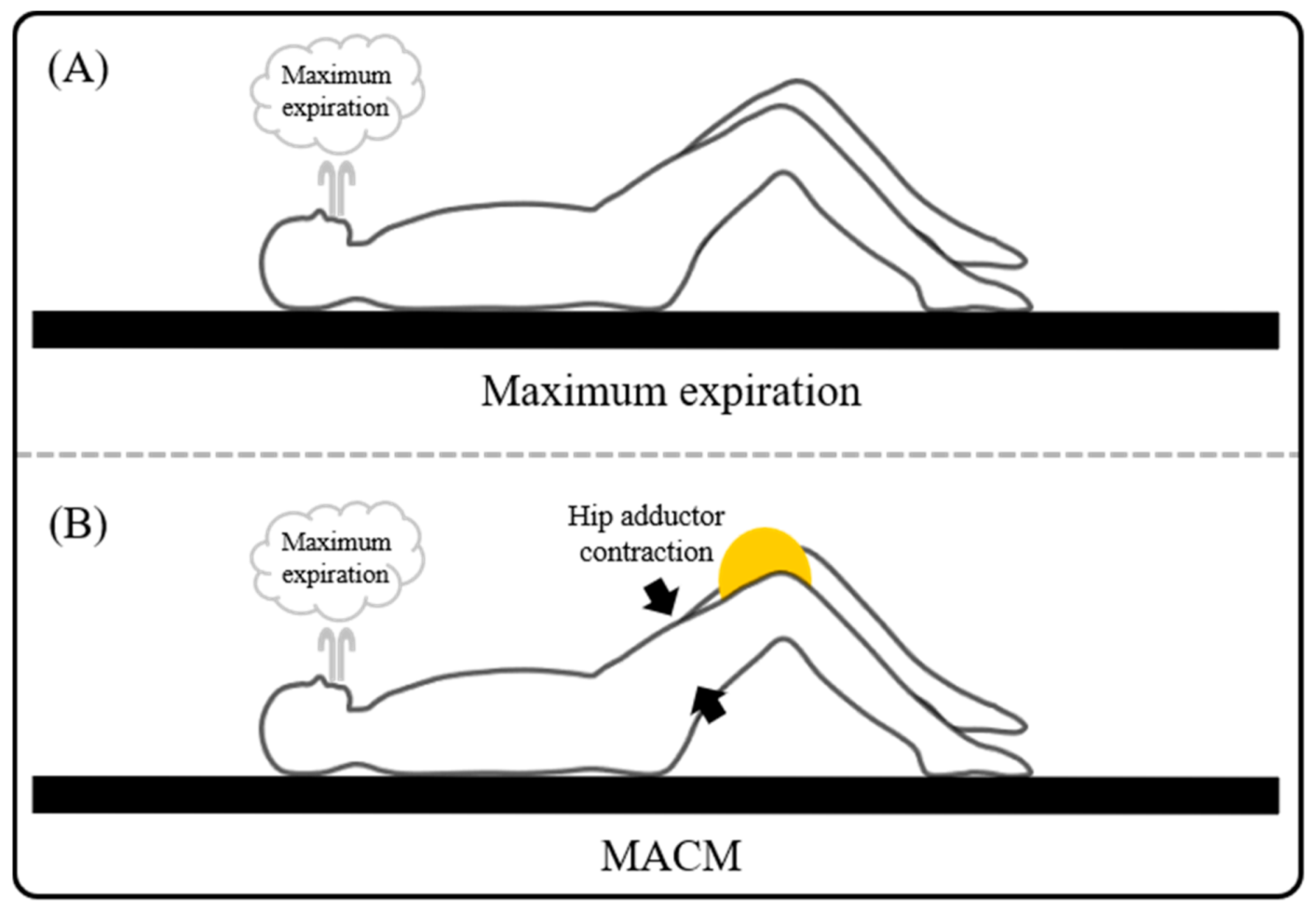
Background and objectives: The maximal abdominal contraction maneuver (MACM) was designed as an effective and efficient breathing exercise to increase the stability of the spinal joint. However, it has not been determined whether MACM is more effective and efficient than the maximal expiration method. Thus, the present study was undertaken to investigate whole abdominal muscle thickness changes after MACM. Materials and Methods: Thirty healthy subjects (17 males and 13 females) participated in this study. An experimental comparison between MACM and the maximal expiration task was conducted by measuring the change of abdominal muscle thickness such as the transverse abdominis (TrA), internal oblique (IO), external oblique (EO) and rectus abdominis (RA) using ultrasound images. Results: The results indicated that MACM resulted in significantly greater muscle thickness increases of the TrA and RA than the maximal expiration exercise (p < 0.05). Conclusion: MACM provided better exercise than the maximal expiration exercise in terms of increasing spine stability, at least from a co-contraction perspective.
[Finn, Dr. Gabrielle M] on . *FREE* shipping on qualifying offers. Know It All Medicine: The 50 Crucial Milestones, Treatments

Know It All Medicine: The 50 Crucial Milestones, Treatments & Technologies in the History of Health, Each Explained in Under a Minute (Know It All, 3)
Download 100,000+ Images From The History of Medicine, All Free Courtesy of The Wellcome Library
Medicina, Free Full-Text

Delsym Adult 12 hour Cough Relief Medicine, Powerful Cough Relief for 12 Good Hours, Cough Suppressing Liquid, #1 Pharmacist Recommended, Orange Flavor, 5 Fl Oz

Instructions for authors - MÆDICA - a Journal of Clinical Medicine
Free Integrative Medicine Class

Search for Articles - Alumni Guide: Library Resources for Public Health Lifelong Learning, Research, Productivity & More - Library Guides at UC Berkeley

Medicina, Free Full-Text, bäumlein 108 led
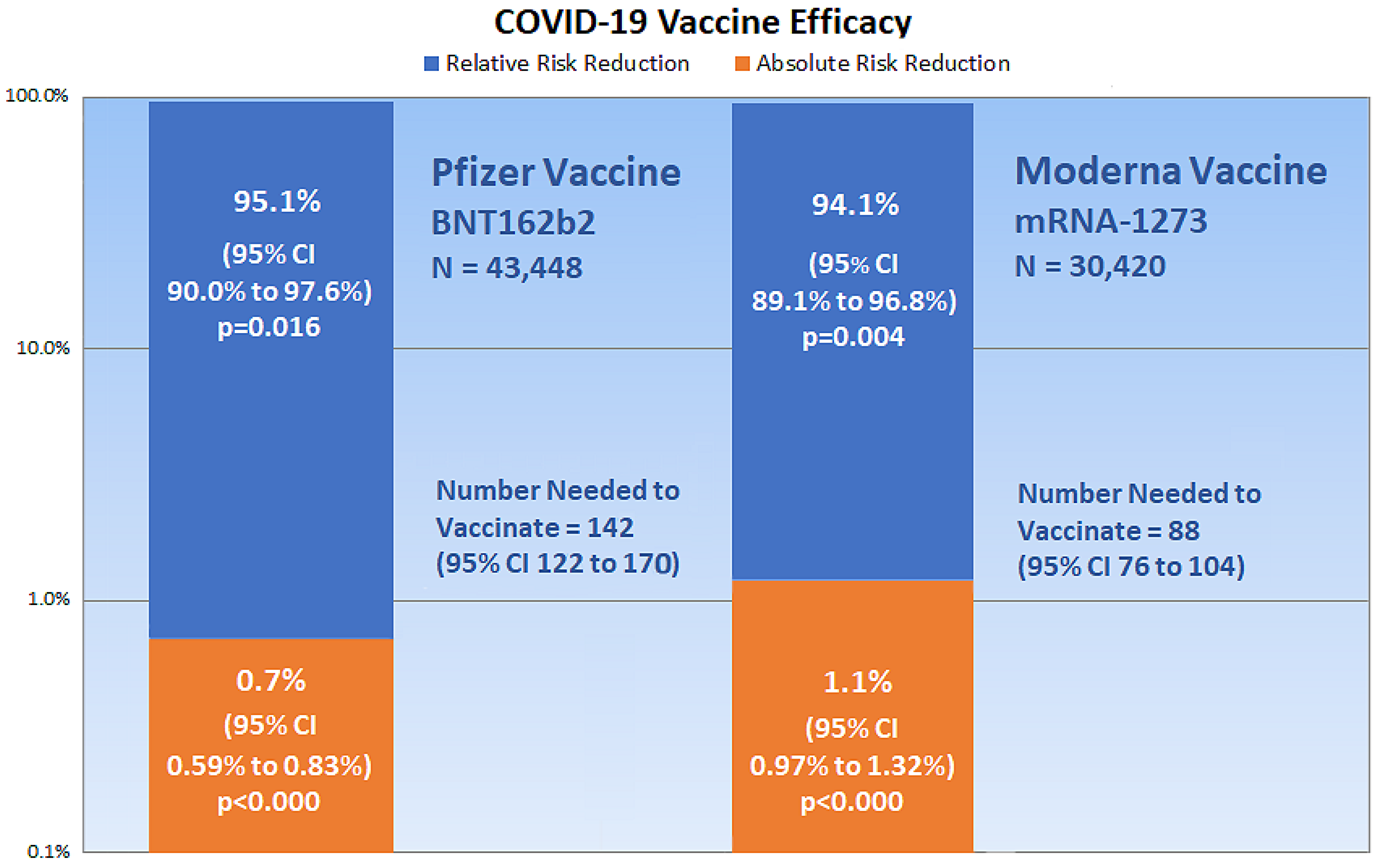
Medicina, Free Full-Text

Library at UM - PubMed Central is a voluminous full-text digital archive of biomedical and life sciences literature. PubMed Central is produced by the U.S. National Library of Medicine. Unlike most medical

PubMed Central® (PMC) - Academic Torrents

Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 - The Lancet, clip
- On Back, Pelvic Floor And Abdominal Contractions by Kelly F

- Feeling the lower abdominal contraction

- New Automatic Rebound Abdominal Fitness Wheel Elbow Support Abdominal Contraction Abdominal Muscle Rolling Abdominal Muscle Slimming Tool Fitness Wheel - China Yoga Mat and Elastic Band price

- belly shape during contraction? (Pic) - April 2018 Babies, Forums

- 1pc Automatic rebound, abdominal contraction, abdominal curling, and abdominal muscle training equipment for men and women's household elbow support, roller sports, and fitness equipment





