Reversible plasticity of detrusor smooth muscle: evidence for a key role of slipping actomyosin cross-bridges in the control of urinary bladder compliance.

By A Mystery Man Writer

Biomechanics of urinary bladder: slow-filling and slow-emptying cystometry and accommodation

ROK-induced cross-link formation stiffens passive muscle: reversible strain-induced stress softening in rabbit detrusor

IJMS, Free Full-Text

Evidence that actomyosin cross bridges contribute to “passive” tension in detrusor smooth muscle

Slowly cycling Rho kinase-dependent actomyosin cross-bridge “slippage” explains intrinsic high compliance of detrusor smooth muscle

Active tension adaptation at a shortened arterial muscle length: inhibition by cytochalasin-D

Slowly cycling Rho kinase-dependent actomyosin cross-bridge “slippage” explains intrinsic high compliance of detrusor smooth muscle

Dynamic protocol for determining APS. Examples of the length-tension

ROK-induced cross-link formation stiffens passive muscle: reversible strain-induced stress softening in rabbit detrusor

PDF] Urinary bladder contraction and relaxation: physiology and pathophysiology.

The Detrusor Muscle: An Innocent Victim of Bladder Outlet Obstruction - ScienceDirect

Frontiers Inhibition of Female and Male Human Detrusor Smooth Muscle Contraction by the Rac Inhibitors EHT1864 and NSC23766

Biomechanics of the urinary bladder: spontaneous contraction activity and micromotions related to accommodation

Isotonic effects of sudden shortening. Left: control contraction at L2
- Time-dependent bladder tissue regeneration using bilayer bladder acellular matrix graft-silk fibroin scaffolds in a rat bladder augmentation model - ScienceDirect

- Giant stones of the urinary bladder with oval shapes, smooth surfaces

- Dog Bladder Control Pills - Pets Urinary Health Complex - for Dogs and Cats - Advanced Bladder Support - Corn Silk Pills for Dogs - 1 Bottle (90 Treats) : Pet Supplies

- Human Bladder Smooth Muscle Cells - Innoprot Bladder Cell System

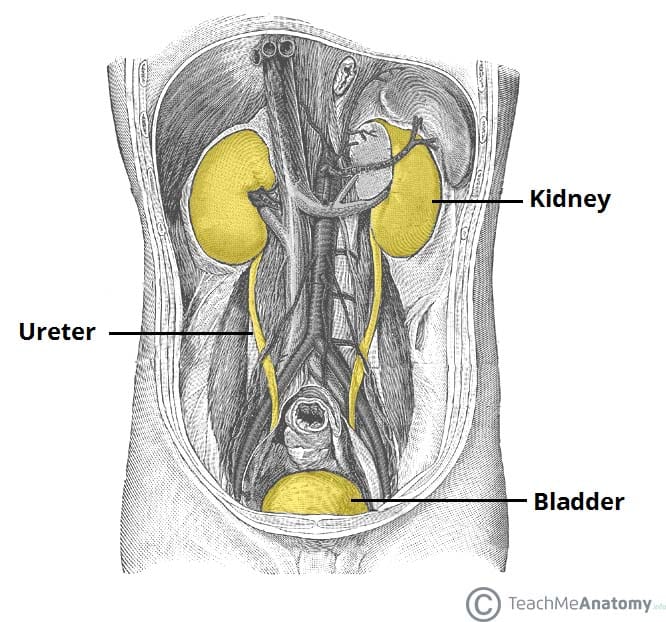
- The Urinary Bladder - Structure - Function - Nerves - TeachMeAnatomy
- Men Quick Dry Short Running Tights Men's Compression Running Shorts Gym Fitness Sport Leggings Male Underwear Sport Shorts - Price history & Review, AliExpress Seller - Shop2183014 Store

- Men'S Triangle Pocket Enhanced Pad 3D Padded Underwear Sexy Sponge Cup
- Women High Waisted Drawstring Side Pocket Plain Full Length

- Prevail Nu-Fit Briefs

- 6PCS Steel Bones Post-Op High Compression Garments Post Surgical Colombianas Faja One Piece Shapewear Legging Pant - China Shapewear Pant and Post Surgical Faja price
