Evaluating coverage bias in next-generation sequencing of
By A Mystery Man Writer
Whole-genome sequencing is essential to many facets of infectious disease research. However, technical limitations such as bias in coverage and tagmentation, and difficulties characterising genomic regions with extreme GC content have created significant obstacles in its use. Illumina has claimed that the recently released DNA Prep library preparation kit, formerly known as Nextera Flex, overcomes some of these limitations. This study aimed to assess bias in coverage, tagmentation, GC content, average fragment size distribution, and de novo assembly quality using both the Nextera XT and DNA Prep kits from Illumina. When performing whole-genome sequencing on Escherichia coli and where coverage bias is the main concern, the DNA Prep kit may provide higher quality results; though de novo assembly quality, tagmentation bias and GC content related bias are unlikely to improve. Based on these results, laboratories with existing workflows based on Nextera XT would see minor benefits in transitioning to the DNA Prep kit if they were primarily studying organisms with neutral GC content.

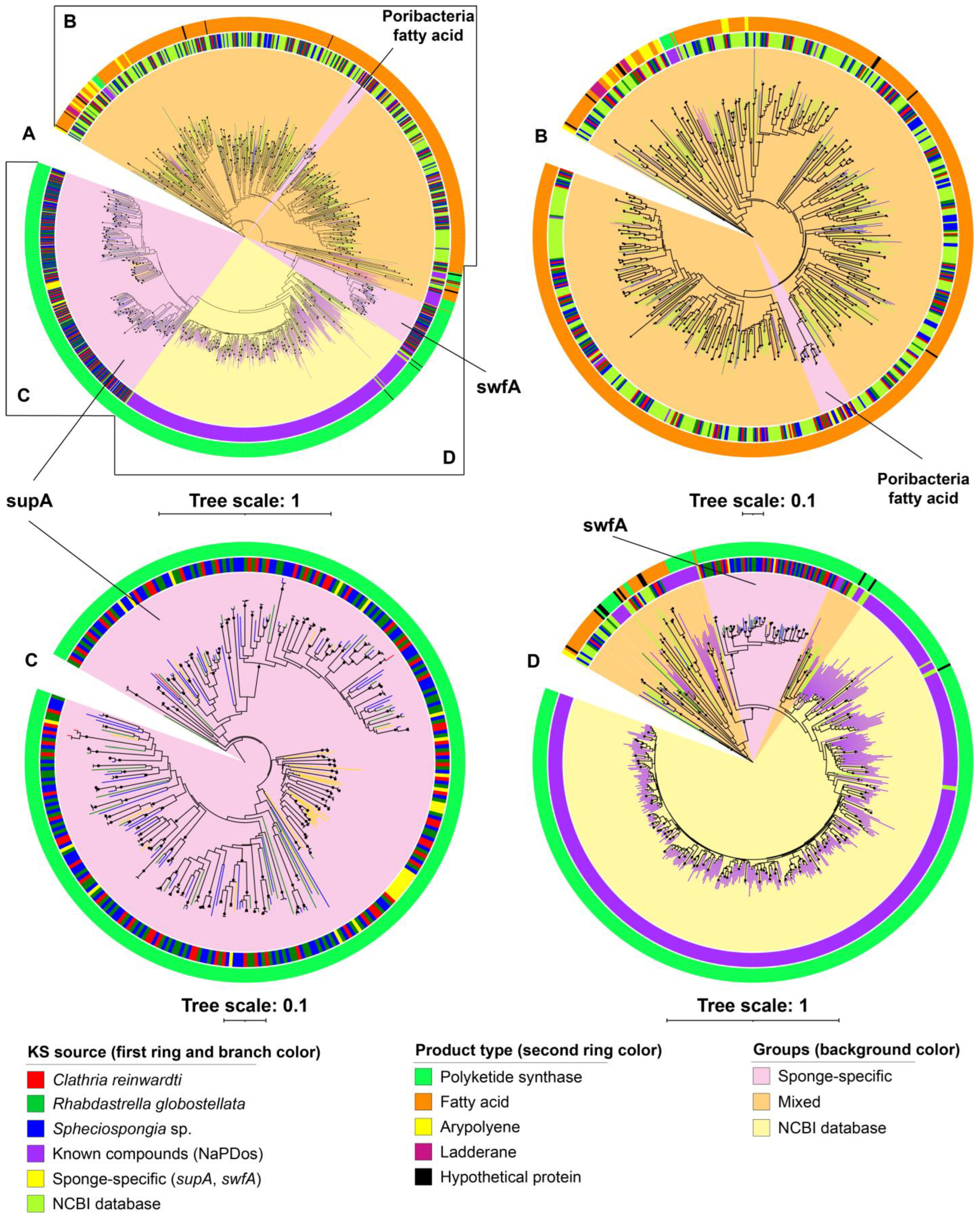
Figure 2 from Summarizing and correcting the GC content bias in

Pathogens, Free Full-Text

Marine Drugs, Free Full-Text

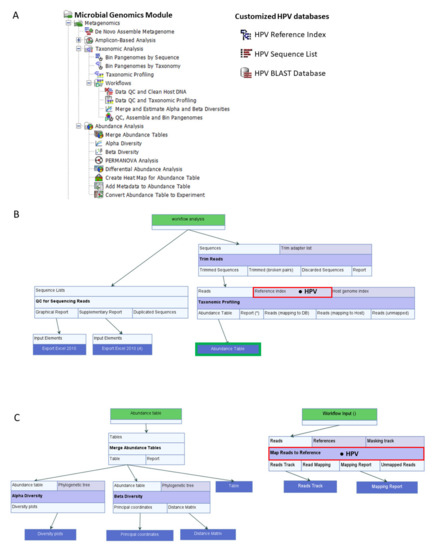
Scheme of sample treatments and library preparation workflow

PDF] Summarizing and correcting the GC content bias in high
Marine Drugs, Free Full-Text

PDF] Summarizing and correcting the GC content bias in high

On-and off-target editing analysis in extraction-free libraries

Raw read quality control parameters. Raw sequence read QC

Phables: from fragmented assemblies to high-quality bacteriophage
Pathogens, Free Full-Text

of serotype predictions that lack an O antigen call by the
- Kia Access app - low network coverage? Anyone else. : r/kia
- How to improve the Wi-Fi® or wireless internet connection to your Roku® streaming device

- Vinyl box truck lettering 26ft low coverage standard

- Jacoco reports low coverage with Compose tests · Issue #1208
- Three Ways Gencove's Low-Pass Whole Genome Sequencing is

- Sofia Jeans Women's Melisa Flare High Rise Coated Pants, 33.5 Inseam, Sizes 2-20

- Molly Smith delighted with 'perfect' breast enlargement after she was trolled over bust size

- Hanes Women's Originals Bralette, Pullover Cotton Longline Bra

- Spanxs TikTok
- BRAZIL Brass plaque celebrating the establishment of the First

