probability - Proof explanation - weak law of large numbers - Mathematics Stack Exchange

By A Mystery Man Writer
Let $(X_i)$ be i.i.d. random variables with mean $\mu$ and finite variance. Then $$\dfrac{X_1 + \dots + X_n}{n} \to \mu \text{ weakly }$$ I have the proof here: What I don't understand is, why it
Has anyone asked a question on math.stackexchange and gotten rude/ condescending answers, for not knowing enough about the subject, and got disheartened from asking math questions anymore? - Quora

real analysis - Proof of the strong law of large numbers for bernoulli random variables - Mathematics Stack Exchange
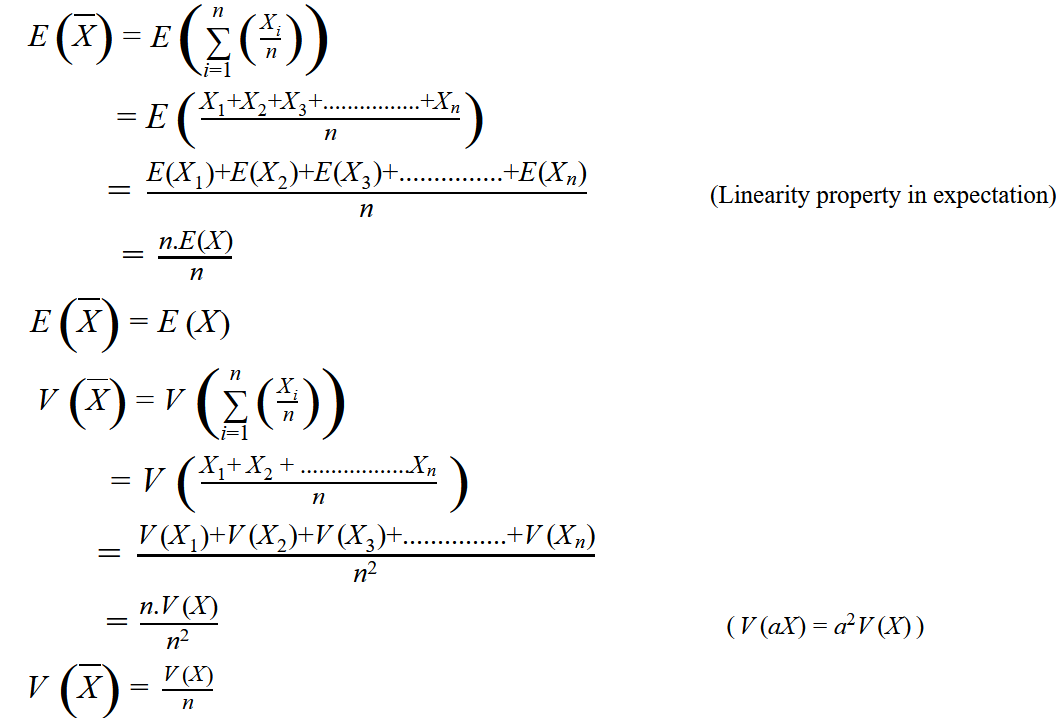
Laws of Large Numbers (detailed explanation), by Anirudh G

The Mystery at the Heart of Physics That Only Math Can Solve

MathType on X: According to the Law of large numbers, the average of the results obtained from several trials tends to become closer to the expected value as more trials are performed. #
Why is it that proof by contradiction is considered a weak proof
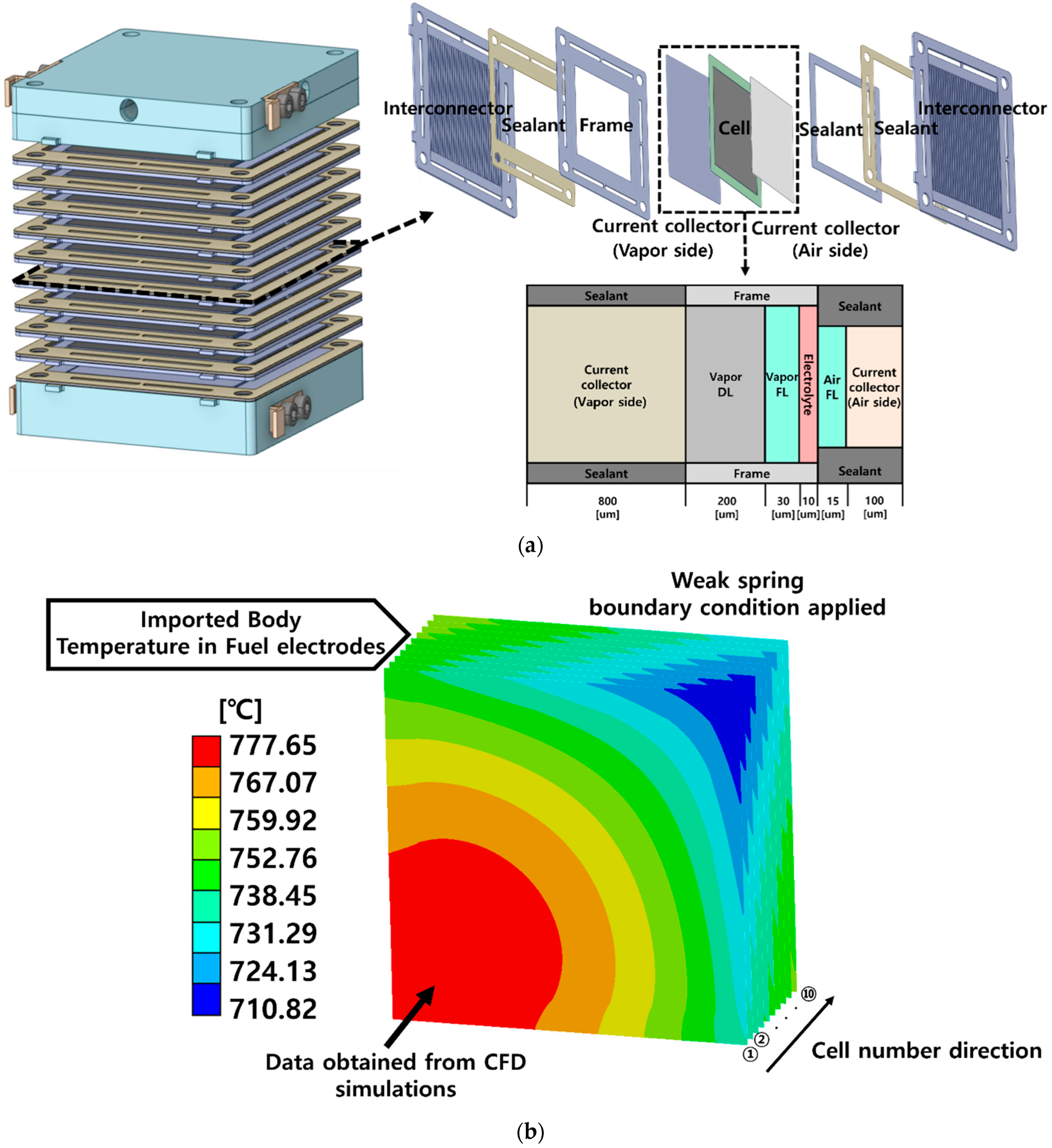
Energies, Free Full-Text

econometrics - Is this use of a Law of Large Numbers correct? - Economics Stack Exchange
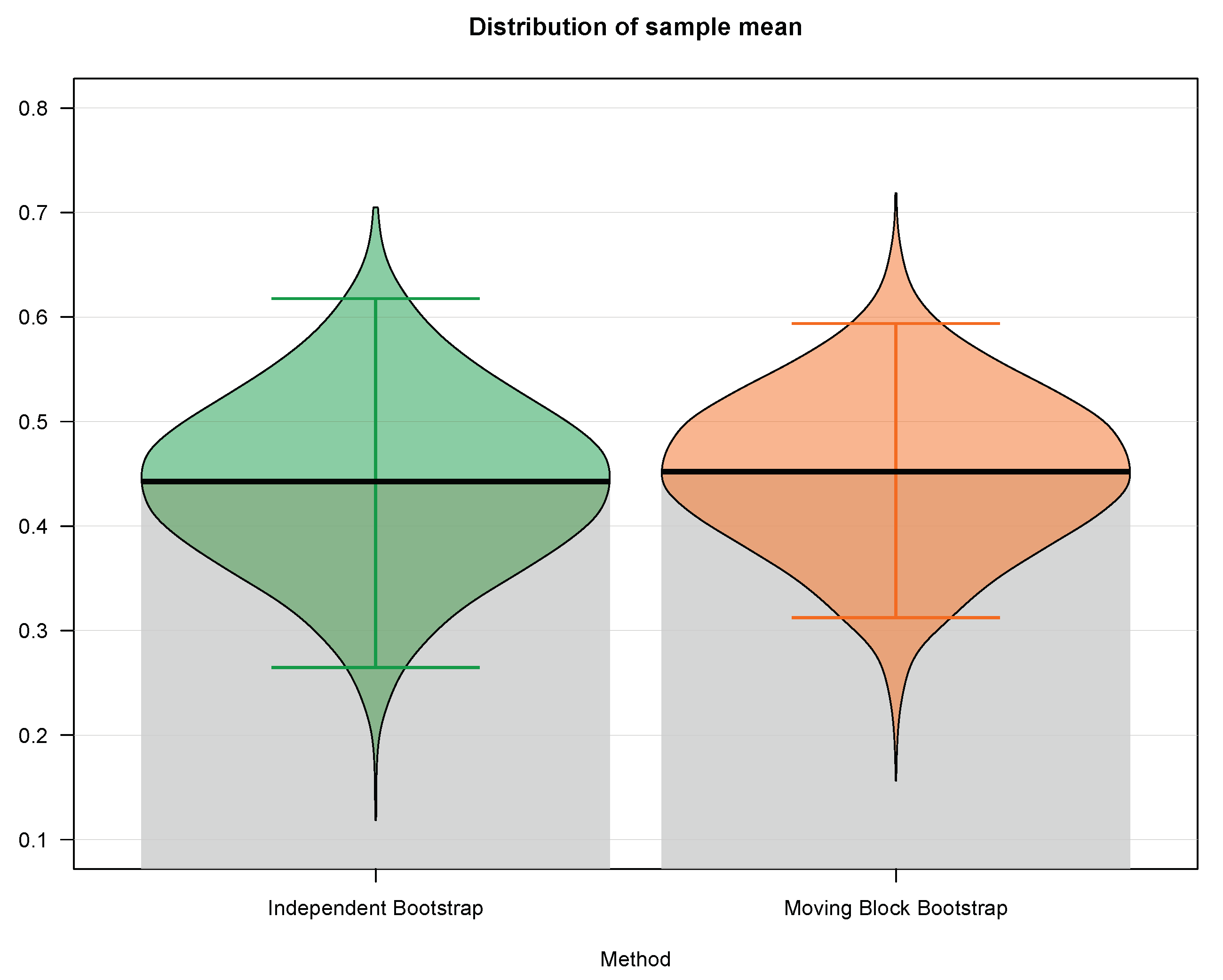
Mathematics, Free Full-Text

How Not to Be Wrong: The Power of Mathematical Thinking: Ellenberg, Jordan: 9780143127536: : Books

Laws of Large Numbers (detailed explanation), by Anirudh G

statistics - Expectation of square of random variable and their mean. - Mathematics Stack Exchange

Distribution (mathematics) - Wikipedia
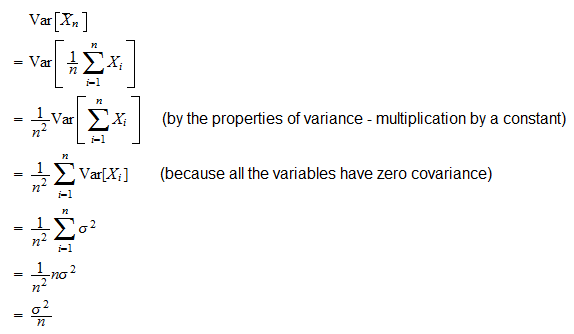
Law of Large Numbers Strong and weak, with proofs and exercises

Proof of the Law of Large Numbers Part 1: The Weak Law
- Lauren Conrad At A Public Appearance For Lauren Conrad Hosts At Tao Beach, Tao Beach At The Venetian Resort Hotel And Casino, Las Vegas, Nv July 31

- Viral TikTok Products That Are Actually Worth the Buy

- Carry Caliber Comparison: .38 Special Vs. 9mm Luger

- Vector De Moda Ropa Bonita Para Las Niñas Ilustraciones svg, vectoriales, clip art vectorizado libre de derechos. Image 64367073

- Generic 36 Inch Synthetic Braided Hair Darkgreen/Green Box Braids
/product/16/5655651/1.jpg?1162)