Proteomic analysis reveals sex-specific biomarker signature in
By A Mystery Man Writer
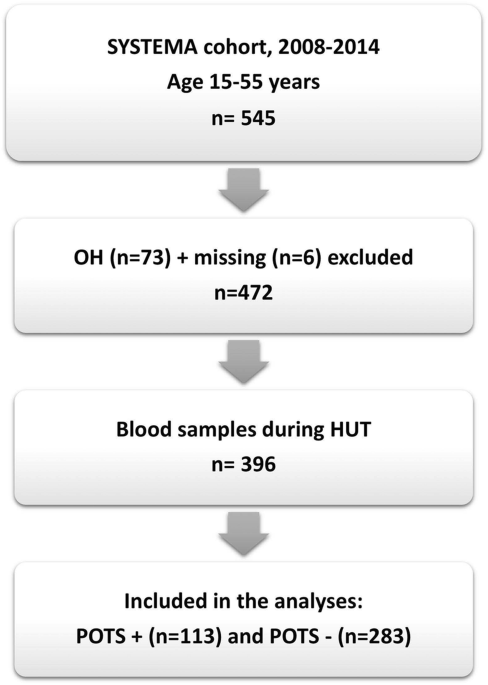
Background Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is a variant of cardiovascular (CV) autonomic disorder of unknown etiology characterized by an excessive heart rate increase on standing and orthostatic intolerance. In this study we sought to identify novel CV biomarkers potentially implicated in POTS pathophysiology. Methods We conducted a nested case-control study within the Syncope Study of Unselected Population in Malmö (SYSTEMA) cohort including 396 patients (age range, 15–50 years) with either POTS (n = 113) or normal hemodynamic response during passive head-up-tilt test (n = 283). We used a targeted approach to explore changes in cardiovascular proteomics associated with POTS through a sequential two-stage process including supervised principal component analysis and univariate ANOVA with Bonferroni correction. Results POTS patients were younger (26 vs. 31 years; p < 0.001) and had lower BMI than controls. The discovery algorithm identified growth hormone (GH) and myoglobin (MB) as the most specific biomarker fingerprint for POTS. Plasma level of GH was higher (9.37 vs 8.37 of normalised protein expression units (NPX); p = 0.002), whereas MB was lower (4.86 vs 5.14 NPX; p = 0.002) in POTS compared with controls. In multivariate regression analysis, adjusted for age and BMI, and stratified by sex, lower MB level in men and higher GH level in women remained independently associated with POTS. Conclusions Cardiovascular proteomics analysis revealed sex-specific biomarker signature in POTS featured by higher plasma level of GH in women and lower plasma level of MB in men. These findings point to sex-specific immune-neuroendocrine dysregulation and deconditioning as potentially key pathophysiological traits underlying POTS.

High-throughput proteomics profiling-derived signature associated

Study protocol for head-up tilt test (HUT)., o que é tilt test

Flowchart of patient selection. HUT indicates headup tilt; OH

Metabolomics reveals sex-specific metabolic shifts and predicts

Clinical Characteristics of the Study Population

PDF) Fasting Levels of High-Sensitivity Growth Hormone Predict Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality The Malmo Diet and Cancer Study

Sex-specific relationship between changes in heart rate during

Potential proteomic biomarkers associated with AD. The diagram
Quantitative proteomics identifies a plasma multi-protein model
- Compression Garment Reduces Orthostatic Tachycardia and Symptoms in Patients With Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome - ScienceDirect

- Living with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS)
- Comorbidities of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome

- POTS (Cf also Dysautonomia)

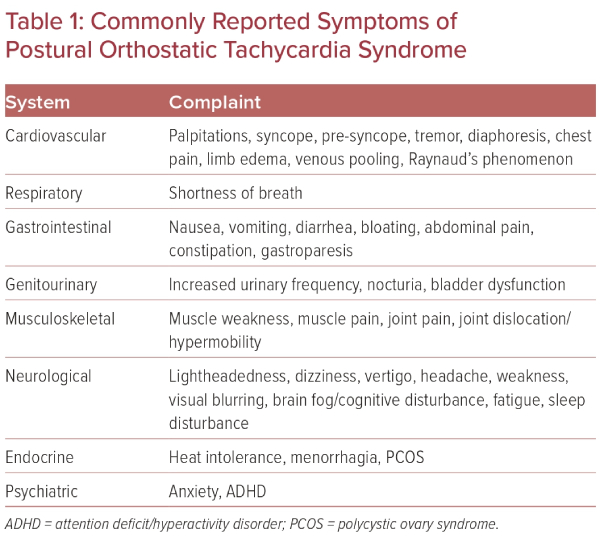
- Commonly Reported Symptoms of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia
- Peloton Fossa Apparel Bomber Jacket Womens Size Small S Black Spell Out Full Zip

- New oysho legging available in brown & Black Size S M L Dm for
- Nike One Plus Size Logo Leggings Womens Dri-FIT 7/8 Mid-Rise

- Women Solid Sports Pants With Pocket Fashion Jogging Sports Sweatpants High Waist Gym Fitness Trousers

- AMVELOP Adjustable Camisole for Women Spaghetti Strap Tank Top Camisoles

